
We will discuss how to calculate the target profit both with and without considering tax rates. With fixed costs and contribution margin ratio in hand, businesses can steer towards their target with confidence. Remember, using this formula isn’t just smart; it’s crucial for growth and stability. We can also determine the number of units that need to be sold to achieve this target profit.
Optimizing Financial Performance Through Sales Mix Variance Analysis
It helps management set profit targets to increase operational efficiency. At this point, the company will earn sufficient revenue to cover all the fixed costs. It also happens to the expense such as rental, utilities, payroll, and other fixed costs, the management needs to ensure that they are not significantly increased during the year. Usually, they overestimate them around 5%-10% base on the nature of business. There are several formulas that can be used to calculate target profit, depending on the information available and the specific context of the business. Target profit is usually determined as part of a business’s budgeting process, and is monitored over the specific period against the actual outcomes.
Equity Turnover Ratio: Comprehensive Guide for Financial Analysis
For example, let’s say a manufacturing company with limited resources is looking to optimise their workforce. It’s not just about picking a number randomly, but instead finding that balance between a price that will attract customers, while also ensuring that price keeps the business profitable. Target profit serves as a crucial reference point for decisions across all areas of a business. The second step is to draw the graph with the cumulative sales showing on the x-axis and the profit on the y-axis. The methods discussed above are useful for a single-product facility or a manufacturing facility with a limited number of products.
- Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections.
- The sales mix refers to the proportion of different products or services that a company sells.
- Without setting time limits the practice of the target profit approach would be futile.
- These steps will help keep financial performance on track and support business growth.
Pricing Strategies
To achieve target profit, businesses must first understand the concept of target profit itself. Target profit is the amount of net income a company aims to achieve over a specific period. This figure is not arbitrary; it is often based on historical data, market conditions, and strategic goals.
Practical Examples of Target Profit Calculation
Let us discuss this desired profit concept and different methods to calculate it. Without target profit, companies may struggle with cost analysis and end up spending too much or earning too little. Notice that to get target profit formulas or equations, we have just included the target profit to break-even point formulas. For instance, in CVP analysis, it is often used as a synonym for operating income. However, it also sometimes means “net income” which could include non-operating expenses, such as interest on debt.
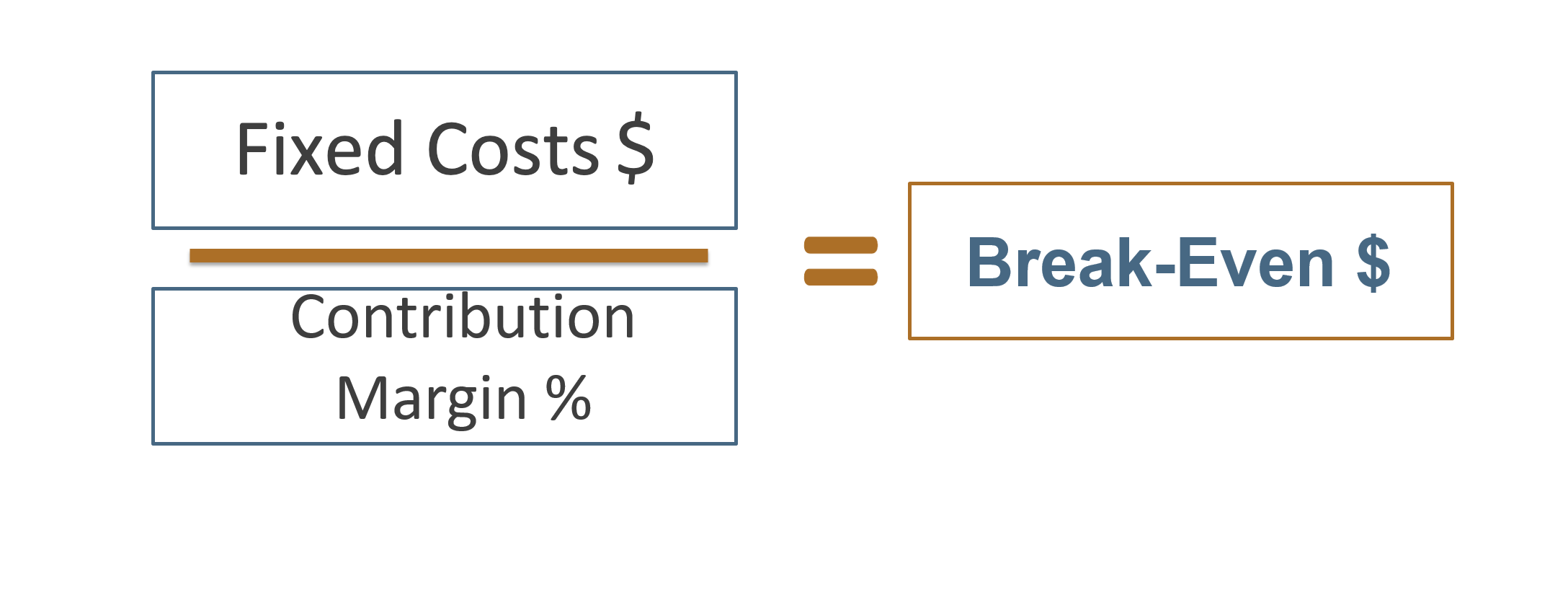
Else, the desired profit amount is set to determine the output quantity or the production volume level. Without setting time limits the practice of the target profit approach would be futile. For instance, a business can set a dollar amount to achieve through increased sales. Delving into the mechanics of target profit calculations, we’ll unpack a methodical approach to pinpoint your financial goals—where precision meets strategy for business triumph.
A variation on the use of the break even formula can be used to determine the revenue needed to achieve a profit target level. The graphical method of the profit-volume analysis assumes that the company must sell its most profitable product first. In the final step, all figures are placed in the following formula to calculate this profit. The management can then add the desired profit that comes through excess of the break-even point sales.
To illustrate the concept and its practicality, we will turn our attention to Adam Electronics, a retailer that specializes in selling tablets. In the world of business and finance, understanding the dynamics of profit is crucial. Businesses aim not only to cover their costs but also to generate a surplus, or profit, as the reward for their efforts.
Target profit is the amount of money a company aims to make from its business activities. The margin of safety in this problem is equal to target sales volume less break even sales volume. The top managements may have no interest in all the figures here, they just want the company to reach a certain of net income during the year.
Production department must keep the cost within the standard cost otherwise it will reduce the profit. They have to control the material wastage, worker idle time and product quality. To illustrate this tax-related complexity, let’s assume a tax rate of 20%. In essence, this means that for every dollar earned as profit, 20 cents must be set aside to cover taxes. If you compared operating income between two similar companies, such as Lowes, Inc. and The Home Depot, Inc., you would be comparing apples to apples. Target profit acts as a benchmark against actual financial performance can be measured.
If the company ABC had set a target point, the crossing point at the x-axis will represent the required sales to achieve that target profit. Yes, the formula can guide you in setting prices by showing what you need to charge to reach your profit goals. The how long does an irs tax audit take is a way to figure out how many things you need to sell to make the money you want. In above CVP chart, red dot represents break-even sales and blue dot represents target sales. We can observe that the corporation breaks even at a sales volume of $1,120,000 and target sales for the next year are $1,680,000 which are $560,000 higher than the break-even sales. This analysis can help to identify high-performing locations and areas that need improvements in order to achieve the target profit.

Leave A Comment